Supporting healthcare decisions in the COVID-19 crisis




A global evidence response to the COVID-19 emergency
Healthcare decisions should be based on a synthesis of the global body of evidence rather than relying on discrete studies. Evidence synthesis methods seek to establish the overall balance of information on a topic, and are based on identifying, assessing and examining all the available evidence on a topic to inform health care decisions.
Evidence Synthesis Ireland, Cochrane Ireland and the HRB Trials Methodology Research Network are national initiatives based at the National University of Ireland Galway. The team are responding to the vast quantities of COVID-19 evidence by addressing key knowledge gaps to support healthcare policy and practice decision-making.
Working with colleagues across the university, the team formed the Emergency Evidence Response Service (EERS) to answer prioritized questions from the World Health Organization (WHO), Cochrane and governments. The team harnessed existing connections and developed new international collaborations to reduce duplication of effort, minimize research waste, share information, and ensure continued capacity building in innovative methodology
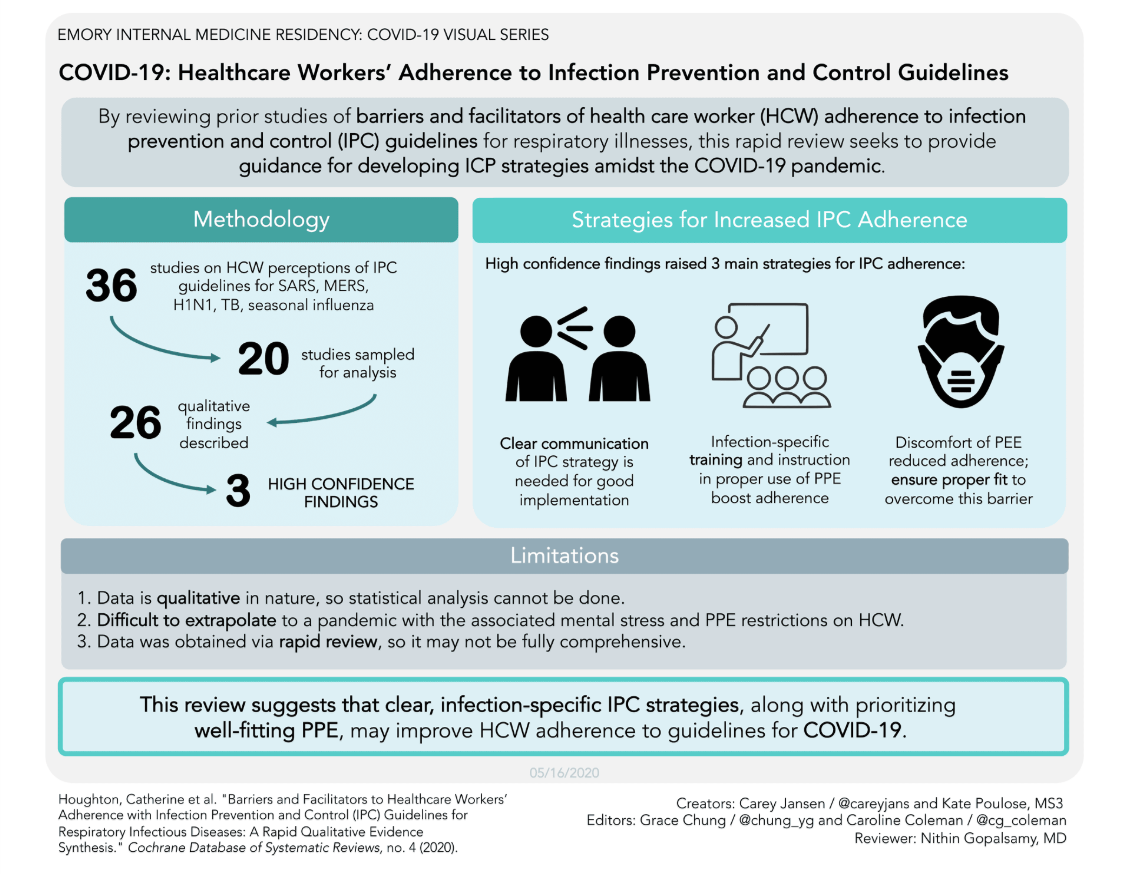
Infection prevention and control guidelines for healthcare workers
Cochrane, a global independent network for trusted evidence, produced a series of rapid reviews of relevant evidence to help decision makers during COVID-19.
One of these looks at the views of healthcare workers on infection prevention and control guidelines, published in April 2020. This work was cited in WHO interim guidance: Prevention, identification and management of health worker infection in the context of COVID-19.
Lead author, Dr. Catherine Houghton from NUI Galway describes the key findings in this podcast.

Podcast: Factors that influence whether healthcare workers follow infection prevention and control guidelines for respiratory infectious diseases by Dr. Catherine Houghton.
Podcast: Factors that influence whether healthcare workers follow infection prevention and control guidelines for respiratory infectious diseases by Dr. Catherine Houghton.
Supporting quality, timely and trustworthy evidence
The team are collaborating on the Covid-19 living network meta-analysis initiative - a live, open mapping of evidence to support decision-makers with relevant, accessible, up-to-date, and trustworthy synthesis of high-quality evidence on the treatment and prevention of COVID-19, including vaccines. The initiative, launched in March 2020 by Cochrane France, is developed and maintained by an international collaborative effort.
WHO use this living evidence ecosystem as their primary source of evidence, and it is also used to inform decision-making in Ireland. This highlights the benefits of contributing to a global initiative to optimise the use of a rapidly-evolving evidence base that answers both international and national questions.
Cochrane Ireland team publish COVID-19 scoping review to inform WHO guidance
Cochrane expanded its response to COVID-19 by publishing rapid scoping reviews which serve as exemplars for how similar research could be published by Cochrane beyond the pandemic.
One of these looks at care bundles for treating patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care setting. The review, published in December 2020, was commissioned by the WHO to use in their Clinical Management living guidance intended for clinicians caring for COVID-19 patients.


Co-author Prof Declan Devane (NUI Galway)
Co-author Prof Declan Devane (NUI Galway)
Extended use or reuse of face masks
Global shortages of PPE forced the consideration of extended use and reuse of face masks. This rapid review was carried out to inform evolving policies and practice and was published in September 2020 in Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.
The review was cited in WHO interim guidance on use of personal protective equipment during severe shortages during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Loneliness in older people: could video calls help?
This Cochrane rapid review searched for randomised trials that looked at the effects on mental health and loneliness of video calls for people aged 65 years or living in nursing homes.
Based on the evidence available at the time of this review, the effects of video calls on the mental health or loneliness of older people are uncertain. More studies testing the effectiveness of video calls for loneliness or isolation are needed. Lead author Dr Chris Noone describes what they found in the podcast.
Trials in a Pandemic
To support the trial methodology community, the HRB-TMRN hosted an online conference on the topic of clinical trials in a pandemic, embracing flexibility and ensuring integrity. In collaboration with Trial Forge, University of Aberdeen, the symposium brought together some of the world’s leading experts, including Dr Ana Maria Restrepo from WHO and Prof Isabelle Boutron, lead of COVID-NMA.
The conference had 1,600 registrations from 23 countries, 10 international speakers, and streamed in 17 timezones
Supporting the public's decision-making
Everyday, claims are made about ways to treat or prevent COVID-19 on social media, some reliable and some unreliable. Unreliable claims can lead to poorly informed health choices. iHealthFacts is a resource where the public can quickly and easily check the reliability of health claims circulated by social media.
iHealthFacts launched in April 2020. As of November 2020, we have had:
- 41,000 unique page views from more than 127 countries;
- 500 health claims submitted and more than 1000 searches about various claims;
- 36 health claims fact checked to date.
- Facebook posts reaching over 10,000 people, 428,00 Twitter impressions and 3,500 Instagram impressions.
Questions the public have asked us to research include ‘Does Chloroquine prevent or treat COVID-19?’, ‘Are face shields as effective as facemasks in protecting against COVID-19? and ‘Does a high BMI increase vulnerability to COVID-19?’


In the media


Claire Byrne Live - 23 Nov 2020
Irish Times - Nurses in the pandemic: ‘Everyone was confused. . . communication was the biggest problem’
Irish Times - Transparent reporting and effective communication strategy need for vaccine roll out
Irish Examiner - Quality of PPE a key issue for healthcare staff worldwide - Galway study
The Times - NUI Galway counters ‘mad’ bleach theories in site tackling Covid fake news infodemic